Demystifying Google ADK
A Simple Guide to the Future of AI Development
Understanding Google’s AI Development Kit through a basic agent implementation
What is Google ADK?
- AI Development Kit from Google
- Makes AI agents easier to build & deploy
- Works with Gemini and other AI models
- Think of it as “Lego blocks for AI”
How It Works (ELI5)
- You type a question in your browser
- Your code in GitHub Codespace gets it
- The ADK agent figures out what you want
- It asks Gemini (via Google Cloud) for help
- Gemini “thinks” and answers
- The reply comes straight back to you!
What is Agent Development Kit? (From Official Google ADK)
Agent Development Kit (ADK) is a flexible and modular framework for developing and deploying AI agents. While optimized for Gemini and the Google ecosystem, ADK is model-agnostic, deployment-agnostic, and is built for compatibility with other frameworks. ADK was designed to make agent development feel more like software development, to make it easier for developers to create, deploy, and orchestrate agentic architectures that range from simple tasks to complex workflows.
Flexible and Modular Framework
- Flexible: Adaptable to different use cases, from simple to complex AI tasks.
- Modular: Built with interchangeable components, so developers can swap or reuse parts.
Developing and Deploying AI Agents
- Developing: Writing the logic and capabilities of AI agents.
- Deploying: Running those agents reliably in different environments like cloud or local machines.
Optimized for Gemini and Google Ecosystem
Designed to work especially well with Google’s Gemini model and tools like Google Cloud.
Model-Agnostic
Can work with other AI models besides Gemini, like OpenAI’s GPT or Anthropic’s Claude.
Deployment-Agnostic
Not tied to any specific platform—you can deploy agents on the cloud, locally, or in apps.
Compatible with Other Frameworks
Easily integrates with other tools and AI frameworks, like LangChain or React frontends.
Feels Like Software Development
Designed so building agents is like building software—structured, testable, and maintainable.
Supports Simple to Complex Architectures
From basic chatbots to multi-agent workflows handling complex tasks.
System Overview
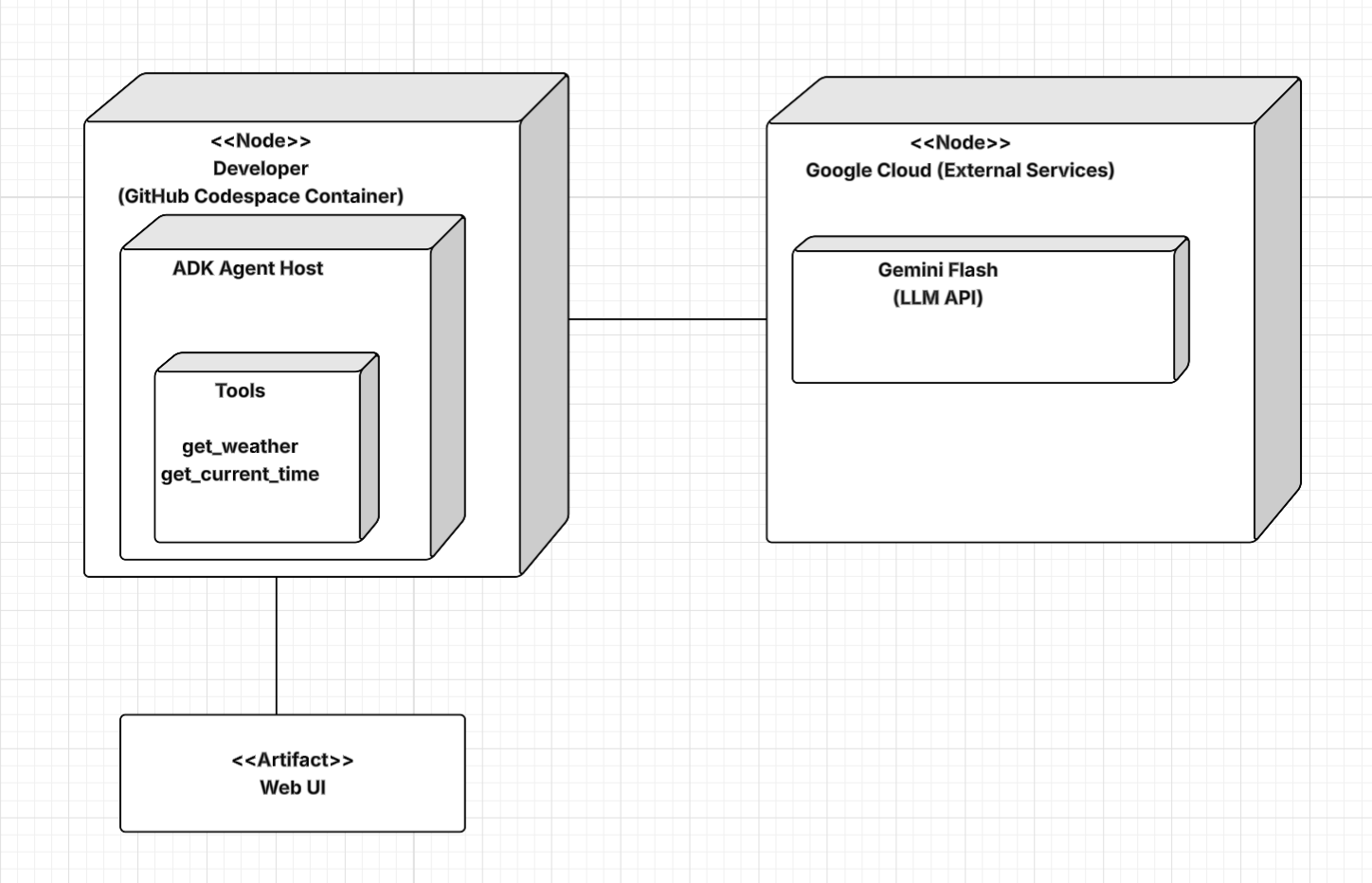
Why It’s Important
For Business
- Faster AI development
- Lower operational cost
- Smooth integration
- Reliable, scalable apps
For Tech Teams
- Standardized building blocks
- Cloud‑agnostic deployment
- Built‑in security patterns
- CI/CD‑friendly workflow
Features
Features
Features
Getting Started (1/3)
Imports & helper libraries
import datetime
from zoneinfo import ZoneInfo
from google.adk.agents import Agent
Getting Started (2/3)
Define your tool functions
def get_weather(city: str) -> dict:
"""Return a mock weather report."""
if city.lower() == "new york":
return {
"status": "success",
"report": (
"The weather in New York is sunny, 25 °C "
"(77 °F)."
),
}
return {
"status": "error",
"error_message": f"No weather data for '{city}'.",
}
def get_current_time(city: str) -> dict:
"""Return the current time in the requested city."""
if city.lower() != "new york":
return {
"status": "error",
"error_message": (
f"Sorry, I don't have timezone info for {city}."
),
}
tz = ZoneInfo("America/New_York")
now = datetime.datetime.now(tz)
return {
"status": "success",
"report": (
f"The current time in {city} is "
f"{now:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %Z%z}"
),
}
Getting Started (3/3)
Create the root agent
root_agent = Agent(
name="weather_time_agent",
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
description=(
"Agent that answers questions about time "
"and weather in a city."
),
instruction=(
"You are a helpful agent who can answer user "
"questions about the time and weather."
),
tools=[get_weather, get_current_time],
)
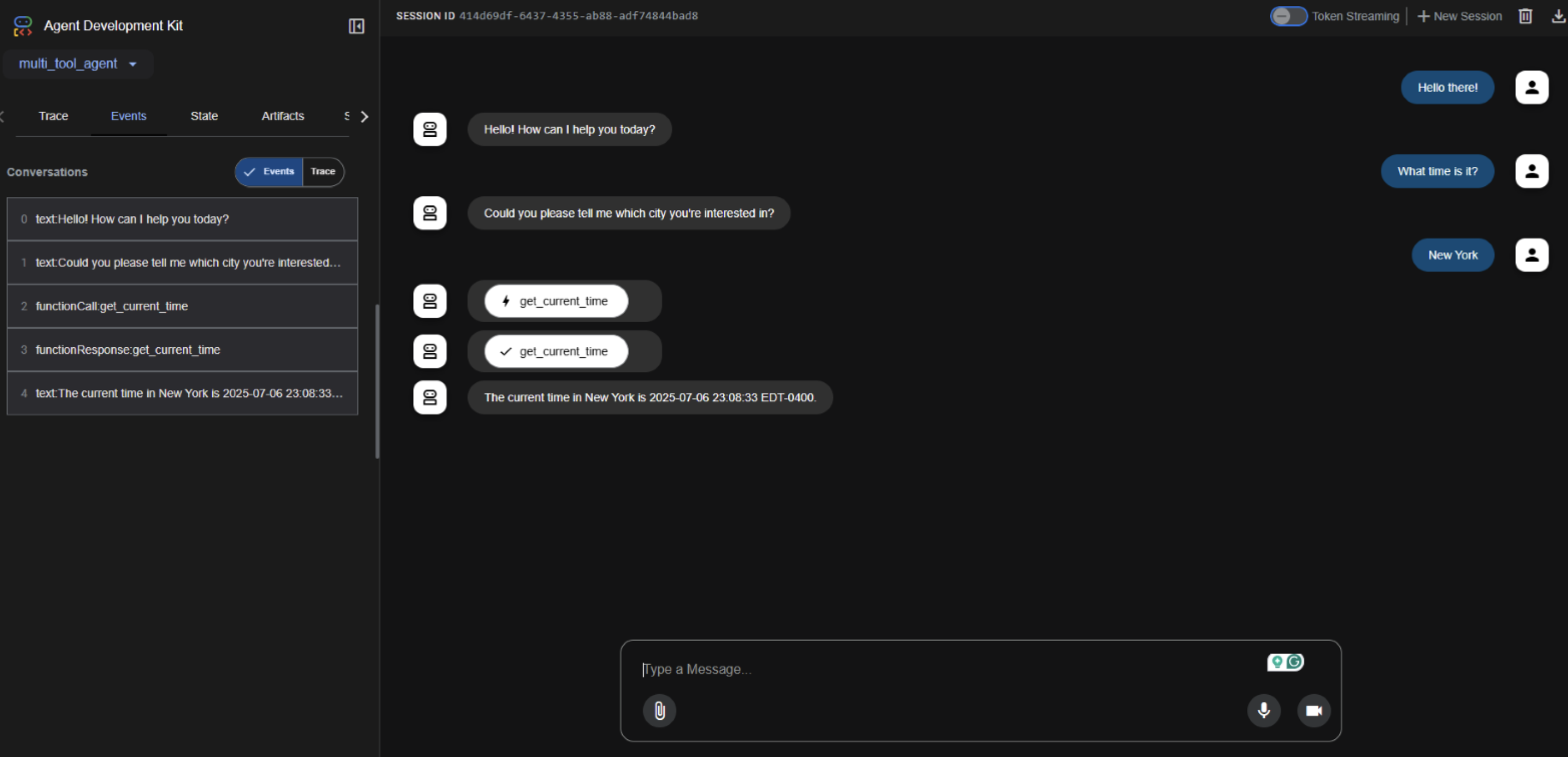
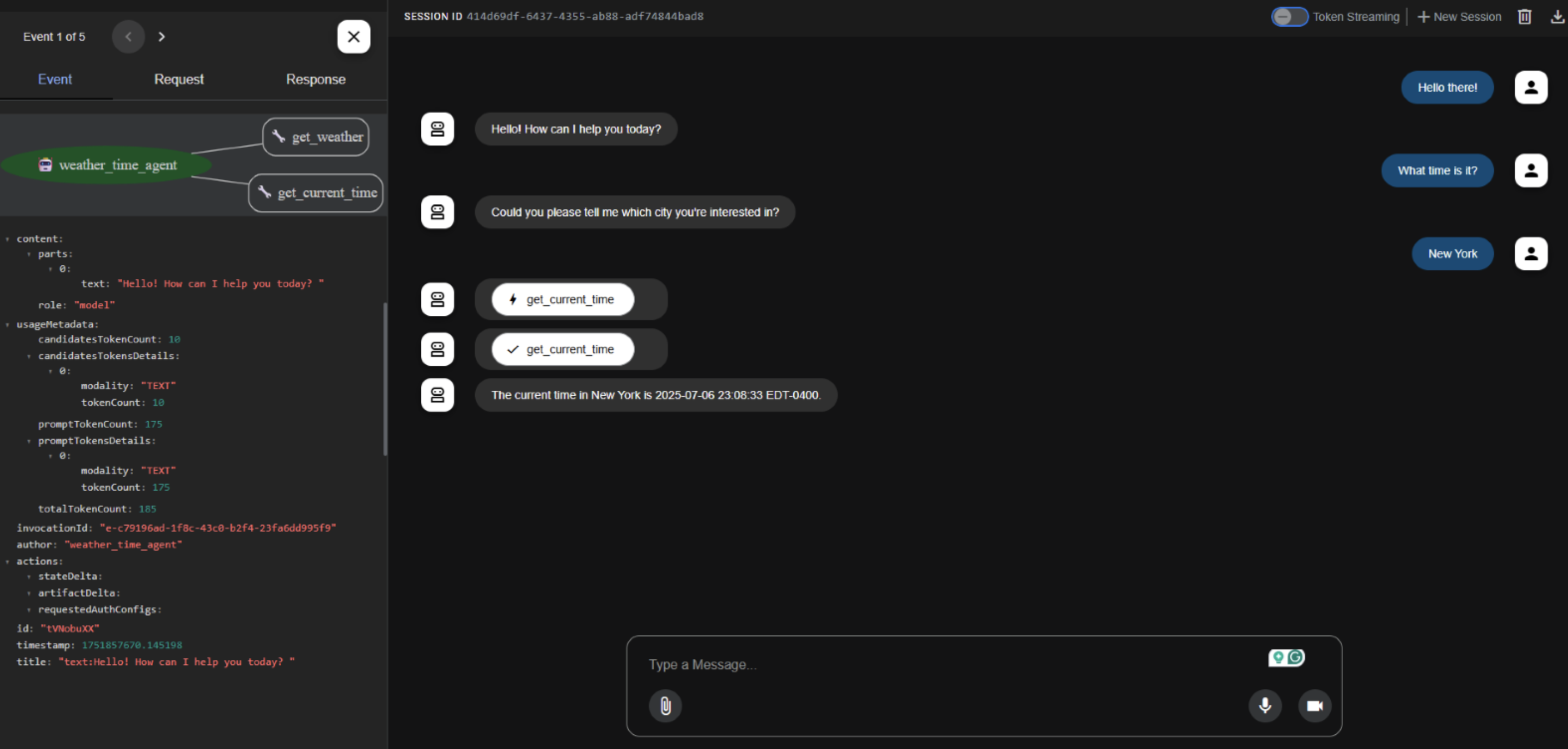
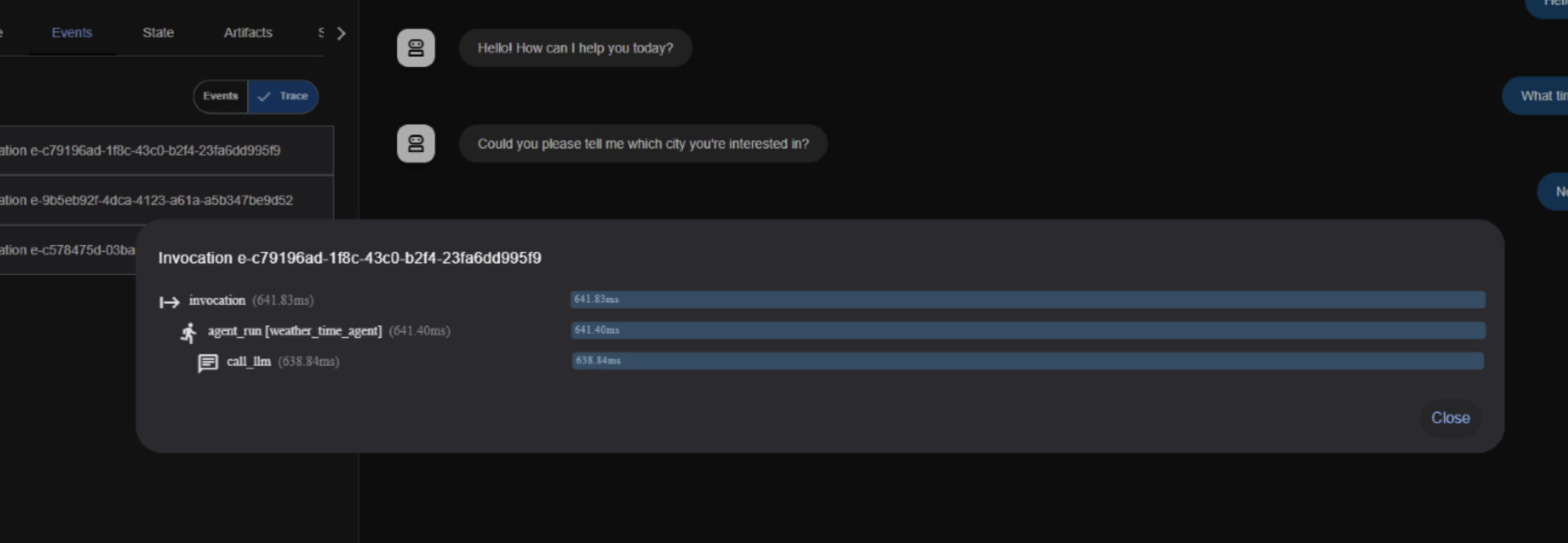
Live Demo
Let’s run root_agent.ask("What’s the weather in New York?")!
(Opening Codespace…)
What’s Next?
- Add new capabilities (vision, search, tools)
- Connect external APIs & databases
- Handle domain‑specific tasks
- Orchestrate multi‑agent workflows
Start small → scale as your needs grow.
References
Thank You!
Questions? Let’s discuss.